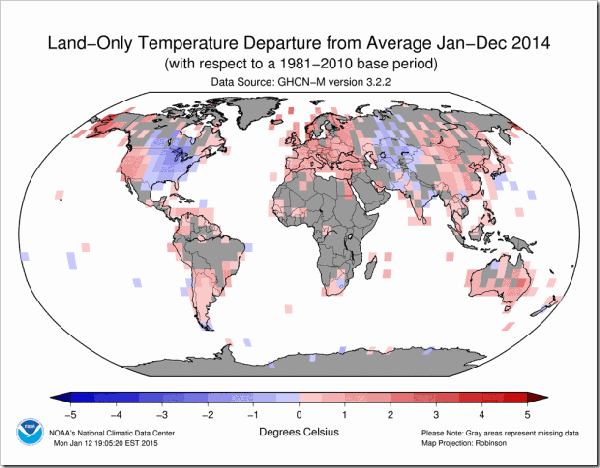
As the global warming matter chugs along, more more evidence of the manipulation of data is coming to light.
Although it has been emerging for seven years or more, one of the most extraordinary scandals of our time has never hit the headlines. Yet another little example of it lately caught my eye when, in the wake of those excited claims that 2014 was “the hottest year on record”, I saw the headline on a climate blog: “Massive tampering with temperatures in South America”. The evidence on Notalotofpeopleknowthat, uncovered by Paul Homewood, was indeed striking.
Puzzled by those “2014 hottest ever” claims, which were led by the most quoted of all the five official global temperature records Nasa’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (Giss) Homewood examined a place in the world where Giss was showing temperatures to have risen faster than almost anywhere else: a large chunk of South America stretching from Brazil to Paraguay.
Noting that weather stations there were thin on the ground, he decided to focus on three rural stations covering a huge area of Paraguay. Giss showed it as having recorded, between 1950 and 2014, a particularly steep temperature rise of more than 1.5C: twice the accepted global increase for the whole of the 20th century.
But when Homewood was then able to check Giss’s figures against the original data from which they were derived, he found that they had been altered.
Some interesting graphics here.
I follow this story on a skeptic blog and Steve McIntyre’s blog.
Both are currently tearing apart an absurd recent paper that has serious statistical errors. Steve is a statistician.
A new paper in Nature by Jochem Marotzke and Piers Forster: ‘Forcing, feedback and internal variability in global temperature trends'[i] investigates the causes of the mismatch between climate models that simulate a strong increase in global temperature since 1998 and observations that show little increase, and the influence of various factors on model-simulated warming over longer historical periods. I was slightly taken aback by the paper, as I would have expected either one of the authors or a peer reviewer to have spotted the major flaws in its methodology. I have a high regard for Piers Forster, who is a very honest and open climate scientist, so I am sorry to see him associated with a paper that I think is very poor, even as co-author (a position that perhaps arose through him supplying model forcing data to Marotzke) and therefore not bearing primary responsibility for the paper’s shortcomings.
This is embarrassing as many are attacking the methods with what sound like valid arguments.
Even Nature has begun to recognize trouble in the alarmist world.
Despite the continued increase in atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations, the annual-mean global temperature has not risen in the twenty-first century 1, 2, challenging the prevailing view that anthropogenic forcing causes climate warming. Various mechanisms have been proposed for this hiatus in global warming3, 4, 5, 6, but their relative importance has not been quantified, hampering observational estimates of climate sensitivity. Here we show that accounting for recent cooling in the eastern equatorial Pacific reconciles climate simulations and observations. We present a novel method of uncovering mechanisms for global temperature change by prescribing, in addition to radiative forcing, the observed history of sea surface temperature over the central to eastern tropical Pacific in a climate model.
The story is getting harder to defend but, grant money being what it is, there is still a strong motive to try to keep the ball rolling, even uphill.
The Michael Mann lawsuit against Mark Steyn and National Review is still chugging along as Mann seems to have nine lives in this matter.
Steyn comes to Washington Tuesday for a hearing at the D.C. Court of Appeals. Michael Mann, a climate scientist at Penn State, filed the lawsuit against Steyn, National Review, space policy and tech analyst Rand Simberg and the Libertarian-bent Competitive Enterprise Institute (CEI) in 2012.
All parties have lawyered up. They all have different legal representation with the exception of Simberg, who is clumped in with CEI.
It is hard for me to take this seriously but there are enough scientifically illiterate judges to keep Mann’s suit alive.
Steyn insists Mann is waiting out the clock so that everyone he’s suing will be good and broke if they ever get remotely near the prospect of a trial. The journalist, however, is plowing ahead, raising money and prepping himself for a trial he’s dying to see happen.
The case is already on its second judge — the first one applied for “senior status” (meaning she’ll work part time and get full pay) and was accepted. The second, says Steyn, seems to be more on top of things, but has been unable to restore a timely process.
Mann appears to be following a “law fare” strategy.
”If this guy Dr. Mann feels he’s being defamed then he should, like Oscar Wilde, get in court and have the manner settled. There is no right to a speedy trial…but you know, defamation is serious and more injurious to one’s reputation than bouncing a check for $30 at the general store. It’s more injurious than a parking ticket, than doing 45 in a 30 mile speed limit. [There’s the right to a speedy trial], but not for defamation. Nuts to that.”
Last summer, a “lukewarmer” scientist named Roger Peilke had the misfortune to encounter the angry left when he accepted a job at the left wing site called five thirty eight.
Roger Pielke Jr. said Monday that he left FiveThirtyEight, ending a short-lived but turbulent stint with the site launched by Nate Silver earlier this year.
Pielke, a professor of environmental studies at the University of Colorado, told Discover Magazine that after editors at the site “showed some reluctance” in publishing his work, he told FiveThirtyEight managing editor Mike Wilson that “it was probably best that we part ways.”
Reluctance was not exactly the proper term. Hysteria was more like it.
“Disinformer!” the Daily Kos screamed. “One of the country’s leading tricksters on climate change,” charged the Huffington Post. “Inaccurate and misleading,” was ThinkProgress’s measured verdict. Even that doyen of professionalism and sworn enemy of hyperbole, Michael Mann, weighed in, knocking his foe for his “pattern of sloppiness.” The pile-on was as predictable as it was unjust. At root, Pielke’s biggest crimes are to have walked at slightly different pace than his peers and to have refused to bow to the president. Pielke accepts the IPCC’s view of the climate-change question but suggests in parallel that man’s response is unlikely to have a “perceptible impact on the climate for many decades” and that civilization should thus adapt to, rather than attempt to prevent, change.
Pielke quickly left. He now has begun a new blog called The Climate Fix.
The alarmist hysteria grows more acute as the evidence piles up that they are wrong and, perhaps, even lying.
