It is amazing the things you find out while writing a book review. In this case, a review of Phillips Payson O’Brien’s How the War Was Won: Air-Sea Power and Allied Victory in World War II. The book is thoroughly revisionist in that it posits that there were no real decisive land battles in WW2. The human and material attrition in those “decisive battles” was so small relative to major combatants’ production rates that losses from them were easily replaced until Anglo-American air-sea superiority — starting in the latter half of 1944 — strangled Germany and Japan. Coming from the conservative side of the historical ledger, I had a lot of objections to O’Brien’s book starting with some really horrid mistakes on WW2 airpower in the Pacific.
You can see a pretty good review of the book at this link — How the War Was Won: Air-Sea Power and Allied Victory in World War II, by Phillips Payson O’Brien
However, my independent research on General MacArthur’s Section 22 radar hunters in the Philippines proved one of the corollaries of O’Brien’s thesis — Namely that the Imperial Japanese were a fell WW2 high tech foe, punching in a weight class above the Soviet Union — was fully validated with a digitized microfilm from the Air Force Historical Research Agency (AFHRA) at Maxwell AFB, Alabama detailing the size, scope and effectiveness of the radar network Imperial Japan deployed in the Philippines.
The microfilm reel A7237 photoshop below is a combination of three scanned microfilm images of an early December 1944 radar coverage map of the Philippines. It shows 32 separate Imperial Japanese Military radar sites that usually had a pair of Japanese radars each (at lease 64 radars total), based upon the Japanese deployment patterns found and documented in Section 22 “Current statements” from January thru March 1945 elsewhere in the same reel.
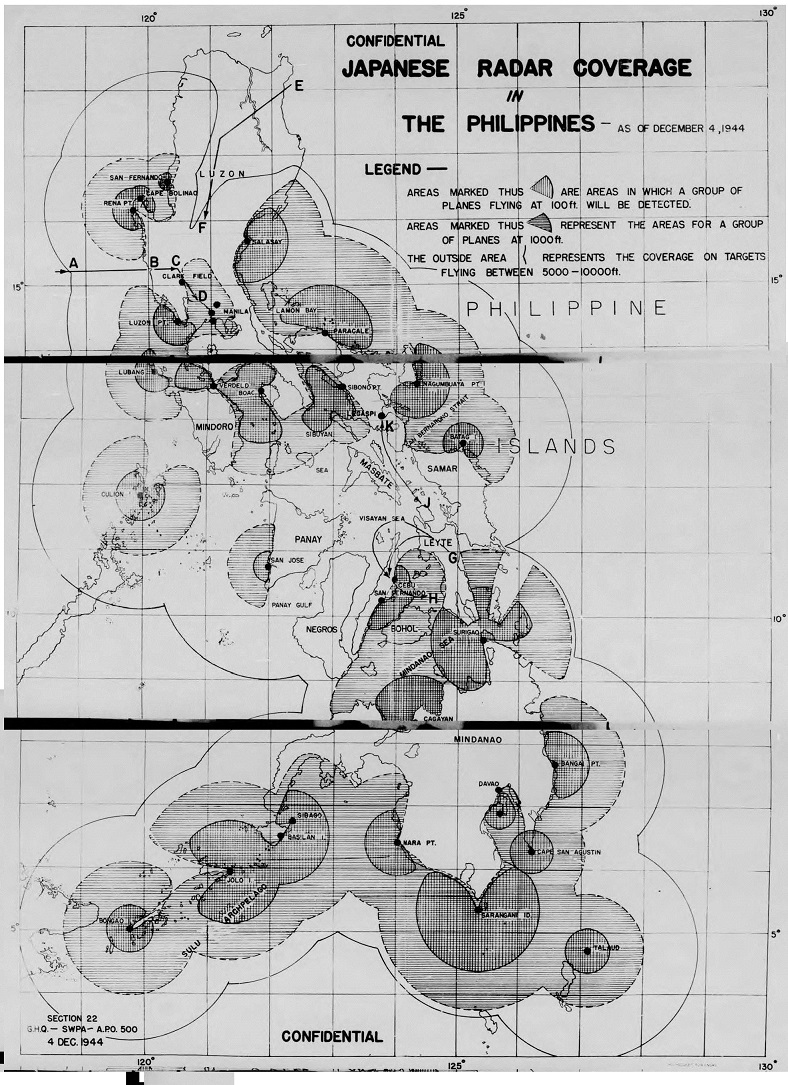
This Section 22 created map — taken from dozens of 5th Air Force and US Navy aerial electronic reconnaissance missions — showed Japanese radar coverage at various altitudes and was used by Admiral Halsey’s carrier fleet (See route E – F on the North Eastern Luzon area of the map) to strike both Clark Field and Manila Harbor, as well as by all American & Australian military services to avoid Japanese radar coverage to strike the final Japanese military reinforcement convoys, “Operation TA”, of the Leyte campaign.