Last week Rick Perry made a comment that got wide attention in mainstream media.
Mr. Perry brought the Fed directly into the campaign debate Monday night by saying it would be “almost … treasonous” for the central bank to play politics by expanding the money supply.
“If this guy prints more money between now and the election,” Mr. Perry said in Cedar Rapids Monday night, without naming Mr. Bernanke, “I don’t know what y’all would do to him in Iowa, but we—we would treat him pretty ugly down in Texas.”
Today, on Meet the Press, Peggy Noonan showed that she is completely clueless on this subject by going off on a riff about how a president has to appear “nice.” She never did address the subject.
Others, who appear to know more about monetary policy had a somewhat different take.
Thomas Gallagher, a principal and economic policy analyst at the Scowcroft Group in Washington who advises Wall Street firms, said Mr. Perry’s comments will be the first thing many investors learn about his candidacy. And the comments are “drawing a fair bit of attention.”
“Voters may not care as much, but investors, like the chattering class, expect a candidate to know what he’s talking about when he talks about the Fed,” he said. “It’s one thing to oppose what the Fed is doing, but it’s another to call it almost treasonous.”
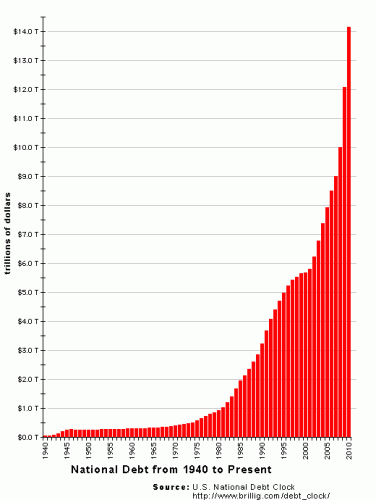
I don’t know that treason was the right word to use but the point is that the Fed is feeding inflation which is far more apparent to those of us who buy our own groceries than most politicians. Ron Paul has been railing at the Fed for years and he is gaining allies.
Libertarian Rep. Ron Paul, who fell 152 votes short of winning the Iowa GOP’s straw poll on Saturday, has been railing against the Fed for years, and former House Speaker Newt Gingrich has joined in with an “Audit the Fed” petition. Other conservatives complain that the Fed’s policy of using monetary policy to stimulate the economy, which it indicated last week it might renew, could be sowing the seeds of inflation.
I would say we are past the “seeds” stage.
The US Treasury has been the largest buyer of new Treasury bonds. How can this be ? The Federal Reserve is printing more money that is then used to buy the debt. Is this an example of the elusive perpetual motion machine ?
Ӣ Turning government bonds into circulating money is called monetizing the national debt.
”¢ Quantitative easing is a euphemism for creating money out of thin air. In the vernacular, we call it “printing money,” even though it really has nothing to do with the U.S. Bureau of Engraving and Printing.
”¢ The way it’s supposed to work is that the Fed buys securities in the open market, paying with a government “check.” (That’s how the money is created.) The sellers deposit those checks into their banks. The banks redeploy those deposits as loans to consumers and business. The money supply expands and, in turn, so does the economy.
What effect will this have on the dollar ? The economy hasn’t exactly expanded while this has been going on.
One factor may be saving us the worst of the effects of this reckless policy. Troubles in Europe and elsewhere in the middle east have caused many investors to engage in a “flight to quality,” although I wouldn’t call the dollar “quality” right now. The Euro, however, seems to be in even worse trouble.
We’ll see what effect Perry’s comment has on his candidacy.