Before there were electronic digital computers, there were mechanical analog computers. Although now obsolete for practical computation, these devices might actually have an useful future ahead of them–in education.
Mechanical analog computation (analog means that calculation is done by measuring rather than by counting) goes back to the Greek Antikythera mechanism (65 BC), which was used to predict the positions of heavenly bodies. The modern era of analog computing began with the work done by James Thompson and his brother William (Lord Kelvin) in the 1870s. First, James Thompson created a mechanical device that performs the calculus function of integration.
Lord Kelvin applied this device…along with other mechanisms for addition and trigonometric functions…to create a mechanical tide-prediction system. These tide predictors had a pretty good run: the invention was announced in 1876, and some of these systems were still in use in the early 1970s!
For those who haven’t studied calculus, integration can be thought of as a kind of continuous addition. Imagine a hose with a fluctuating flow rate filling a pool: by integrating the rate of flow, you can calculate the volume of water added to the pool.
The basic concept of a mechanical integrator is shown below.
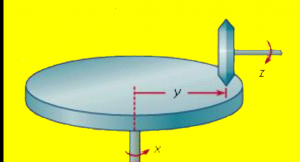
If the vertical shaft is turned at a constant rate, and the small wheel is moved in and out according to the changing value of some some variable Y, then the rotation of the horizontal shaft Z will represent the integral of Y with respect to time. If Y is the rate of flow of the a hose, Z will be the total volume added to the pool. If Y represents the acceleration of a vehicle, then the output shaft will give that vehicle’s speed at any moment. Connect the output to the input of another integrator, and you will get the distance traveled.
Vannevar Bush, who would become Roosevelt’s science adviser during WWII, combined the integrator and other computing mechanisms to create a highly general mechanical computer, called a differential analyzer. Completed in 1931, it was not restricted to a single application, but could be programmed–with a wrench and screwdriver to alter the connections–for a wide range of problems. Complex chains of calculation were possible, including the ability for a result at one stage to be fed back as input at an earlier stage–for example, the speed of a simulated vehicle affects its air resistance, which in turn influences its acceleration…which integrates back to its speed.

Other differential analyzers were built in the U.S., Norway, and Britain, and were used for applications including heat-flow analysis, electrical network stability analysis, soil-erosion studies, artillery firing table preparation, and studies of the loading and deflection of beams. It is rumored that a British analyzer was used in the planning for the bouncing-bomb attack on German hydroelectric dams during WWII. Differential analyzers appeared in several movies, including the 1951 film When Worlds Collide (video clip). The ultimate in mechanical analog computation was the Rockefeller Differential Analyzer, a rather baroque (and very expensive) machine built in 1942. It was decommissioned in 1954, on the belief that the future of calculation would belong to the electronic computer, and especially the electronic digital computer. Following the decommissioning, the mathematician Warren Weaver wrote:
It seems rather a pity not to have around such a place as MIT a really impressive Analogue computer; for there is vividness and directness of meaning of the electrical and mechanical processes involved… which can hardly fail, I would think, to have a very considerable educational value. A Digital Electronic computer is bound to be a somewhat abstract affair, in which the actual computational processes are fairly deeply submerged.