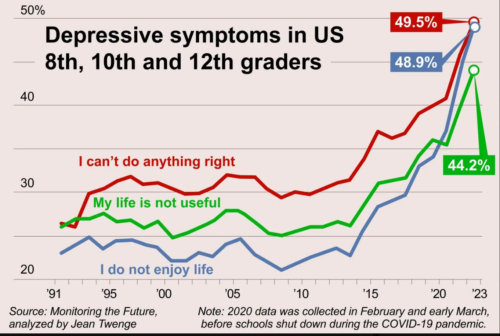
From cdrsalamander at Twitter, based on an analysis of Monitoring the Future survey data by Jean Twenge.
Thoughts?
Some Chicago Boyz know each other from student days at the University of Chicago. Others are Chicago boys in spirit. The blog name is also intended as a good-humored gesture of admiration for distinguished Chicago School economists and fellow travelers.

From cdrsalamander at Twitter, based on an analysis of Monitoring the Future survey data by Jean Twenge.
Thoughts?
The tunic was found in the Norwegian mountains. Textile historians recreated it using the technologies current when it was made–pulling the wool naturally rather than shearing, spinning it into thread (with no spinning wheel), and weaving it into cloth. The labor required was estimated by having skilled people do a sample amount of each task required and extrapolating to the complete garment.
Total labor requirement was 780 hours. The linked post estimates the cost at almost $38000, apparently assuming Norwegian labor rates.
I don’t think anyone would produce such garments using such expensive labor, though (unless it was for some very affluent niche market) but would use cheaper Asian or South American or even American labor. Maybe a reasonable number including overhead and supervision would be something like $5/hour. Which still gives a cost of $3800.
And if someone made it for their own use, or that of someone in their family, that 780 hours would represent a pretty large piece of their work capacity for the entire year.
As Paul Graham noted, clothing was very expensive right up to the Industrial Revolution.
Like all intelligent men who are not in any way creative, Sir Robert Peel was dangerously sympathetic towards the creations of others. Incapable of formulating a system, he threw himself voraciously on those he came across, and applied them more vigorously than would their inventors.
–Andre Maurois
I don’t know enough about Sir Robert to have an opinion about whether this was a fair assessment of him, but I think it’s a valid and important point in general. “Intelligent but not creative” describes a high percentage of people in academia, ‘nonprofits’, and the media (as long as you don’t set bar for ‘intelligent’ too high, especially in the case of the media)…and I think this has a lot to do with their eager adoption of theoretical frameworks such as critical race theory, cultural Marxism, and various types of gender theorizing…and the special and often weird vocabularies that tend to go with such things.
The need to conform, the desire to promote oneself and to feel superior, and the search for meaning also play a part, of course.
See Lead and Gold, which is why I discovered the Maurois quote in the first place. As LG notes, the voracious-framework-adoption phenomenon is also found in business, though at a somewhat lesser level than in academia, media, and nonprofits, I think, due to the exigencies of competition and the need to deal with reality sufficiently well to actually produce products and services.
See also my post Professors and the Pornography of Power, which cites Jonathan Haidt on what he calls the single-lens approach.
Previous Worth Pondering post.
Coming soon: Personal Area Networks.
New Zealand may adopt a new science curriculum that doesn’t have much actual science in it:
Central concepts in physics are absent. There is no mention of gravity, electromagnetism, thermodynamics, mass or motion. Chemistry is likewise missing in action. There is nothing about atomic structure, the periodic table of the elements, compounds or molecular bonding,” he said of the draft.
Rather than physics, chemistry, and biology, the document proposes teaching science through four contexts that appear to draw from fundamental principles of the United Nation’s Agenda 21: climate change, biodiversity, infectious diseases, and the water, food, and energy nexus.
Sounds a lot like the science curriculum that was proposed in the UK circa 2005:
Instead of learning science, pupils will “learn about the way science and scientists work within society”. They will “develop their ability to relate their understanding of science to their own and others’ decisions about lifestyles”, the QCA said. They will be taught to consider how and why decisions about science and technology are made, including those that raise ethical issues, and about the “social, economic and environmental effects of such decisions”.
They will learn to “question scientific information or ideas” and be taught that “uncertainties in scientific knowledge and ideas change over time”, and “there are some questions that science cannot answer, and some that science cannot address”. Science content of the curriculum will be kept “lite”. Under “energy and electricity”, pupils will be taught that “energy transfers can be measured and their efficiency calculated, which is important in considering the economic costs and environmental effects of energy use”. (The above is from John Clare’s article in the Telegraph.)
According to Melanie Phillips: “The reason given for the change to the science curriculum is to make science ‘relevant to the 21st century’. This is in accordance with the government’s doctrine of ‘personalised learning’, which means that everything that is taught must be ‘relevant’ to the individual child.”
2005 was a long time agoI don’t know whether or not this curriculum is still in place in the UK; I use it as an example because it makes a certain kind of thinking very clear. The class is not really about Science, it is about ‘Society’, and everything that is taught must be ‘relevant’ to the child.
And, closer to home, California has a new math curriculum. While math teaching certainly could use improvement, I don’t have a good feeling about this program…see for example this and this, also these comments.
Also, the curriculum includes “data science” as an alternative to Algebra II…see this critique: “Here’s the issue: the data science course is not a good path to a career in data science…It’s math lite for kids who don’t expect to use much math in life. And that’s fine!…as long as the kids KNOW that’s what they’re signing up for. But it’s not being sold that way — it’s being sold as a way to get more kids into data science. …and that’s misleading.”
An actual San Francisco data analytics guy offers this detailed analysis and critique of the curriculum.
Here’s a post with a rather arresting title from a few days ago at Ricochet: She’s a brilliant teacher, perhaps she should stop. At a BBQ, the writer encountered a teacher from his high school days.
Besides my mother, she is the best teacher I’ve ever had. She taught me Physics and Inorganic Chemistry. And the way she taught — understanding rather than memorization — allowed me to ace science and math classes in college and medical school. She helped me so, so much.
She is now 61 years old and is considering retirement. She moved from my public school to a private school, but it’s still wearing her down. She complains that modern students lack curiosity and motivation, while administration and parents pressure her to just give everyone A’s. She teaches how to understand science and math — but they just want her to stamp her approval on their resume. She’s growing increasingly frustrated, to the point where she doesn’t want to go to work anymore.
This is a different problem from the problems of deliberately-weakened curricula, but the root is the same: the belief that acquisition of knowledge is not what matters, rather, what matters is moving through the system and getting that piece of paper. (And, in the case of many updated curricula, ideological indoctrination is also a key objective)