What you are witnessing in the UK is not a crisis. It is a success. When most geographical units secede from a larger entity, they do so unilaterally, and sometimes violently. They do it through war or, if lucky, soft power. The UK is doing everything in accord with publci int’l law, EU law, and its domestic legal system. No armies involved. No violence. No threats of violence. Just elections. It is democracy and it is messy. It compares well to our war dead in 1776 and 1861. The world should be taking lessons–not mourning Brexit.
History
Book Review: The Year of the French (rerun)
The Year of the French, by Thomas Flanagan
(This being St Patrick’s day, I’m again taking advantage of the hook to re-post this review, in the hope of inspiring a few more people to read this incredibly fine historical novel)
Ralph Peters calls this book “the finest historical novel written in English, at least in the twentieth century,” going on to say “except for ‘The Leopard,’ I know of no historical novel that so richly and convincingly captures the ambience of a bygone world.”
In August of 1798, the French revolutionary government landed 1000 troops in County Mayo to support indigenous Irish rebels, with the objective of overthrowing British rule in Ireland. The Year of the French tells the (fictionalized but fact-based) story of these events from the viewpoint of several characters, representing different groups in the complex and strife-ridden Irish social structure of the time.
Owen MacCarthy is a schoolmaster and poet who writes in the Gaelic tradition. He is pressed by illiterate locals to write a threatening letter to a landlord who has evicted tenants while switching land from farming to cattle-raising. With his dark vision of how an attempt at rebellion must end“In Castlebar. They will load you in carts with your wrists tied behind you and take you down to Castlebar and try you there and hang you there”MacCarthy is reluctant to get involved, but he writes the letter.
Sam Cooper, the recipient of the letter, is a small-scale landlord, and captain of the local militia. Indigenously Irish, his family converted to Protestantism several generations ago to avoid the crippling social and economic disabilities imposed on Catholics. Cooper’s wife, Kate, herself still Catholic, is a beautiful and utterly ruthless woman…she advises Cooper to respond to the letter by rounding up “a few of the likeliest rogues,” jailing and flogging them, without any concern for actual guilt or innocence. “My God, what a creature you are for a woman,” Cooper responds. “It is a man you should have been born.” “A strange creature that would make me in your bed,” Kate fires back, “It is a woman I am, and fine cause you have to know it…What matters now is who has the land and who will keep it.”
Ferdy O’Donnell is a young hillside farmer on Cooper’s land. Far back in the past, the land was owned by the O’Donnell family…Ferdy had once shown Cooper “a valueless curiosity, a parchment that recorded the fact in faded ink the colour of old, dried blood.”
Arthur Vincent Broome is a Protestant clergyman who is not thrilled by the “wild and dismal region” to which he has been assigned, but who performs his duties as best he can. Broome is resolved to eschew religious bigotry, but…”I affirm most sincerely that distinctions which rest upon creed mean little to me, and yet I confess that my compassion for their misery is mingled with an abhorrence of their alien ways…they live and thrive in mud and squalour…their music, for all that antiquarians and fanatics can find to say in its flavor, is wild and savage…they combine a grave and gentle courtesy with a murderous violence that erupts without warning…”’
Malcolm Elliott is a Protestant landlord and solicitor, and a member of the Society of United Irishmen. This was a revolutionary group with Enlightenment ideals, dedicated to bringing Catholics and Protestants together in the cause of overthrowing British rule and establishing an Irish Republic. His wife, Judith, is an Englishwoman with romantic ideas about Ireland.
John Moore, also a United Irishman, is a member of one of the few Catholic families that have managed to hold on to their land. He is in love with Ellen Treacy, daughter of another prominent Catholic family: she returns his love, but believes that he is caught in a web of words that can only lead to disaster. “One of these days you will say a loose word to some fellow and he will get on his horse and ride off to Westport to lay an information with Dennis Browne, and that will be the last seen of you”
Dennis Browne is High Sheriff of Mayo…smooth, manipulative, and devoted to the interests of the very largest landowners in the county, such as his brother Lord Altamont and the mysterious Lord Glenthorne, the “Big Lord” who owns vast landholdings and an immense house which he has never visited.
Randall MacDonnell is a Catholic landowner with a decrepit farm and house, devoted primarily to his horses. His motivations for joining the rebellion are quite different from those of the idealistic United Irishmen…”For a hundred years of more, those Protestant bastards have been the cocks of the walk, strutting around on acres that belong by rights to the Irish…there are men still living who remember when a son could grab his father’s land by turning Protestant.”
Jean Joseph Humbert is the commander of the French forces. A former dealer in animal skins, he owes his position in life to the revolution. He is a talented commander, but the battle he is most concerned about is the battle for status and supremacy between himself and Napoleon Bonaparte.
Charles Cornwallis, the general who surrendered to the Americans at Yorktown, is now in charge of defeating the French and the rebels and pacifying the rebellious areas of Ireland. Seen through the eyes of a young aide who admires him greatly, Cornwallis is portrayed as a basically kindly man who can be hard when he thinks it necessary, but takes no pleasure in it. “The color of war had long since bleached from his thoughts, and it remained for him only a duty to be scrupulously performed.”
This book is largely about the way in which the past lives on in the present, both in the world of physical objects and the world of social relationships. Two characters who make a brief appearance are Richard Manning, proprietor of a decrepit and debt-laden castle, and his companion Ellen Kirwan:
The June 1944 Normandy Invasion and the Bane of Technologically Illiterate Military Leaders in the Luftwaffe
This blog post on “The June 1944 Normandy Invasion and the Bane of Technologically Illiterate Officers in the Luftwaffe” marks the second in a series of posts departing from past history columns I’ve written for Chicagoboyz in that it is exploring a theme I refer to as “The Bane of Technologically Illiterate Military Leaders.”[1] .
The issue with ‘Technologically Illiterate Military Leaders‘ I’ll be exploring in this and future articles is that such leaders tend to make the same classes of mistakes over and over again. And when those military leaders reach flag rank on the bones of theories and doctrines that fail the test of combat through their technological illiteracy. They then bury the real reasons why those doctrines failed behind walls of jargon and classification to avoid accountability for those failures.
In this particular case, the mistake is how the otherwise technically competent Luftwaffe Funkaufklärungsdienst (Roughly translated — Electronic Intelligence Early Warning Service) managed to miss a completely unambiguous invasion warning for the Normandy Invasion — D-Day, June 6th 1944 — the night before the invasion.
This happened because the German officers over the Luftwaffe technicians were technologically illiterate regards both the Allied identification friend or foe (IFF) and Allied radio navigation systems they were monitoring, as well as the radar techniques their own Luftnachrichten Dienat (Air Surveillance Service) were using to track RAF Bomber Command night bomber streams through chaff.
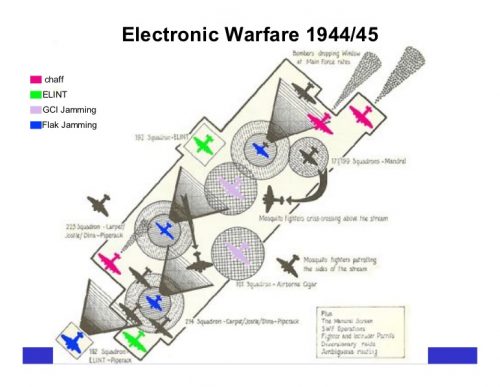
.
Electronic warfare is much like mine sweeping/hunting at sea, or combat engineers breaching a minefield on land, in that it is a thankless job when it is done right and “hard” on military officers careers in exercises/planning. Thus it tends to be avoided, even when it is central to recorded military history. Case in point — When Stephen L. McFarland wrote “Conquering the Night: Army Air Forces Night Fighters at War” in the late 1990’s (pub date 1998) as a part of “AIR FORCE HISTORY AND MUSEUMS PROGRAM.” He completely left out the fact that German bomber tail warning radars were picking up Allied night fighter IFF challenges. This was a fact that Alfred Price had published fourteen years earlier in 1984!
Some thoughts about Churchill, who is under attack these days.
I am currently reading Andrew Roberts’ excellent biography of Churchill.
It does a better job with his early life than the other biographies I have read. I am 2/3 through it and have not yet reached Pearl Harbor so the emphasis is clear. I have reflected on a couple of items, not necessarily about Churchill but about his times.
Churchill was an observer in the Boer War but had some adventures, which included being captured and escaping from a POW camp.
For example, had Cecil Rhodes and the British gold miners not invaded the Transvaal would the Boer War have occurred and, if it had not occurred, would Germany have built its High Seas Fleet?
Now the Transvaal Republic might, like the Orange Free State, have simply remained as a small shut-in self-governing state without creating any disturbance. But the Transvaalers were the sons of the stalwarts who fifty years before had sought to escape from all British control. They looked upon South Africa as a Dutch not a British inheritance; they resented the limitations imposed on them by the British, and their experience had not taught them any respect for the British Empire. Their president, Paul Kruger, had himself gone on the great trek in his boyhood. It is not possible to doubt that President Kruger dreamed his own dreams of a United South Africa, but a South Africa under a Dutch flag, not under the Union Jack; though how far those dreams were shared by others is not equally clear. But whatever his ambitions outside the Transvaal, within the borders of the republic he intended to go his own way.
But then gold was discovered in Transvaal.
In 1885, however, the discovery was made of valuable goldfields within the territories of the republic; aliens, Uitlanders as they were called, for the most part British subjects, whatever their actual nationality might be, poured into the Transvaal to exploit the mines. The Boer government had no objection to the exploitation of the mines on its own terms, which did not include the concession of citizenship to the Uitlanders till after a very prolonged residence. All the burdens of citizenship were laid on the Uitlanders without its privileges. The Uitlanders began to feel that they had no security for justice, and to demand approximately the opportunities for acquiring citizenship in the Transvaal which were readily accorded to the Transvaaler who migrated into British territory.
The “After Big Week” Assessment, plus 75 years
Today marks the 75th Anniversary of the completion of Operation Argument otherwise known as BIG WEEK. The strategic goals of the operation were to destroy German fighter production and inflict a “wastage” rate of the German fighter force such that it was losing fighter planes faster than it was producing them. In measurements of this objective. In the initial assessments of the BIG WEEK bombing, 8th Air Force thought they had done that. Actually, this was as wildly optimistic as the claims of air to air kills by the heavy bomber crew machine gunners.
.
Despite destroying 70% of the German fighter aircraft assembly buildings targeted. The USAAF high command had grossly underestimated damage done to electric motor powered machine tools within those buildings and the UK’s Ministry of Economic Warfare that the USAAF relied upon for intelligence of German industry had underestimated German fighter production by a factor of 2 & 1/2 times.
See my Jan 1, 2019 Chicagoboyz post “Industrial Electrification and the Technological Illiteracy of the US Army Air Corps Tactical School 1920-1940” for many of the reasons why this was so.

The 8th Air Force lost 565 heavy bombers shot down or scrapped from combat damage so bad it was not worth the effort to repair them. 8th and 9th Air Force fighters escorting the bombers suffered 28 planes shot down. The over all loss rate per raid averaged 6%…but the American total force losses were 2,600 air crew killed, wounded or captured. This was 1/5th of 8th Air Force.