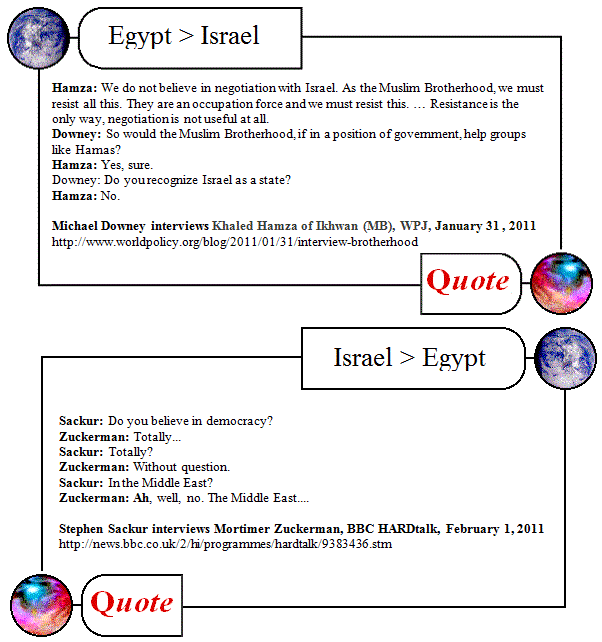
[ by Charles Cameron – cross-posted from Zenpundit ]
*
The description of Egyptian troops attacking a Christian monastery that forms the first quote in this DoubleQuote is horrifying in many ways.
Recent events in Egypt had featured mutual support between Muslims and their Coptic Christian neighbors, each group in turn acting as human shields to protect the other while they were praying. Here, by contrast, the army which is effectively now “ruling” Egypt in the interregnum between the fall of Mubarak and the election of a new President and government is attacking the humans it is supposed to protect.
But what does that have to do with Bach?
*
Part I: a monastery attacked in Egypt
This is vile.
Those who are being attacked happen to be Christians and monks, no less human on either account, and just as subject to bleeding as others so they might ask, with Shakespeare‘s Shylock speaking for the Jews:
If you prick us do we not bleed? If you tickle us do we not laugh? If you poison us do we not die? And if you wrong us, shall we not revenge?
That last question of Shylock’s is an interesting one, and gets to the heart of what I want to discuss here, as we shall see.
Specifically, these human beings were monks. Muhammad had a higher opinion of monks than of many others. In the Qur’an, we find:
The nearest to the faithful are those who say “We are Christians.” That is because there are priests and monks among them and because they are free of pride.
*
Sigh.
These “followers” of Muhammad were attacking Christian monks with live ammunition and RPGs continuously for 30 minutes, wounding 19.
They felt superior to their compatriots the monks, they cried “God is Great” and “Victory, Victory” as they did it.
In this they resemble GEN Boykin, who famously responded to a Somali warlord claiming that God would protect him, “Well, you know what? I knew that my God was bigger than his. I knew that my God was a real God and his was an idol.”
I could easily have made that my second quote here, pairing it with the description of the Egyptian army attack on the monastery, for between the two of them they raise the question of whether weaponry is stronger than belief and while some Christians might agree with General Boykin, some Muslims might agree no less strongly with the members of the Egyptian military shouting “Allahu Akbar”.
*
I believe that taking sides here misses the point.
Which I am happy to say, Abraham Lincoln made with considerable eloquence in his Second Inaugural Address in 1865, almost a century and a half ago:
The prayers of both could not be answered. That of neither has been answered fully. The Almighty has His own purposes.
That point is one which HaShem made to his angels, according to rabbinic teaching:
The Talmud teaches us that on the night that the Egyptian army drowned in the Red Sea, the first true moment of freedom for the Jews fleeing Egypt, God refused to hear the angels sing their prayers, and said “my creations are drowning in the sea, and you will sing songs?”
So, no — revenge is not the way to go…
*
But please note that the point I am making is not one of moral equivalence.
That God which created “both sides” in any human conflict and loves each and every one of his own creations, might indeed find one creed superior to another, as he might find one scientific law more accurately describing the workings of, say, gravitational attraction than another or the night sky at Saint-Rémy portrayed by Van Gogh more or less moving than the thunderous sky over Toledo of El Greco.
In the view I am proposing, the “God who takes neither side” in fact takes both, but with this distinction: he sides with the wounded more than with those who inflict wounds not because one side has a better creed than the other, but because he made us to learn not to unmercifully maim and destroy one another…
…one of whose names is The Merciful, in whose scriptures it is written:
If thou dost stretch thy hand against me, to slay me, it is not for me to stretch my hand against thee to slay thee: for I do fear Allah, the cherisher of the worlds.
…one of whose names is The Lord is Peace, in whose scriptures it is written:
Love your enemies and pray for those who persecute you.
*
Part II: Bach and contrapuntal analysis
All of which brings me to the second “quote” in my DoubleQuote above: JS Bach‘s “concordia discors” canon in two voices, BWV 1086 which you can hear or purchase here.
Bach’s mastery was in counterpoint, the play of one musical idea against another, and in this particular work, the two ideas are exact opposite: in musical terms, the melody is played here against its inversion. And the point of counterpoint, if I may put it that way, is not to provide “harmony” but to show how discord can become harmonious and concordant — or to put that in the geopolitical terms that interest me, how conflict and opposition can be resolved…
Not, you understand, that this state of affairs then leads necessarily to the singing of Kumbaya or the kind of ending in which “they all lived happily ever after”.
Concordia discors: the resolution of the present conflict, in a continuing overall “music” of great power and beauty, in which further conflicts will inevitably arise and find resolution.
*
Here’s the essence: Bach takes contrasting and at times conflicting melodic ideas and makes music.
He teaches us to hear distinct and differing voices, to allow ourselves to hear and feel both the discomfort that their disagreements raise in us, and the satisfaction that comes as those disagreements are worked out. He does this by teaching us to hear them as voices within a choir, ribbons in a complex braid, making together a greater music that any of them alone could give rise to. And in this process, their differences are neither denied nor lost, but resolved and transcended.
Edward Said, whose politics my readers may dislike or like or even perhaps be unaware of, was for years the music critic for The Nation, wrote three books (and an opus posthumous) on music, and with his friend the pianist and conductor Daniel Barenboim co-founded the West-Eastern Divan Orchestra, named for the West-östlicher Diwan, Goethe’s collection of lyric poems.
Barenboim (the Israeli) wrote of Said (the Palestinian):
In addition to being well versed in music, literature, philosophy, and the understanding of politics, he was one of those rare people who sought and recognized the connections between different and seemingly disparate disciplines. His unusual understanding of the human spirit and of the human being was perhaps a consequence of his revelatory construct that parallels between ideas, topics, and cultures can be of a paradoxical nature, not contradicting but enriching one another.
And there we have it again: Bach’s insight, this time transposed by an accomplished musician into the key of thoughts and ideas…
*
Said talks quite a bit about counterpoint, both musically:
Musically, I’m very interested in contrapuntal writing, and contrapuntal forms. The kind of complexity that is available, aesthetically, to the whole range from consonant to dissonant, the tying together of multiple voices in a kind of disciplined whole, is something that I find tremendously appealing.
[Said, Power, Politics and Culture, p. 99.]
and politically:
When you think about it, when you think about Jew and Palestinian not separately, but as part of a symphony, there is something magnificently imposing about it. A very rich, also very tragic, also in many ways desperate history of extremes — opposites in the Hegelian sense — that is yet to receive its due. So what you are faced with is a kind of sublime grandeur of a series of tragedies, of losses, of sacrifices, of pain that would take the brain of a Bach to figure out. It would require the imagination of someone like Edmund Burke to fathom.
[Said, Power, Politics and Culture, p. 447.]
*
As I commented in an earlier post that ties in with this one, the great pianist Glenn Gould was also preoccupied with counterpoint, both in Bach’s music and in conversations overheard at a truck-stop cafe or on long train journeys — he too was “working” the parallel between melodic and verbal forms of counterpoint.
And JRR Tolkien made the reconciliation of discordant musics in a greater concord the central to his creation myth in The Silmarillion, “The Music of the Ainur”, which can now be read online at the Random House site.
*
Part III: invitation
May I strongly commend to your attention the movie, Of Gods and Men, which just opened in limited release, having won the grand jury prize at Cannes…