War and Peace
Welcome to “Section 22 Week,” Day Three
Welcome to the third post in the “Section 22 Week” count down to the Bilge Pumps podcast with the Section 22 Special Interest Group e-mail list. By way of background, the Section 22 ‘SIG’ started in March 2015 with myself as list administrator and later as the groups cloud drive guru. The list accomplished it’s goal of mapping the Australian, New Zealand and American archives for Section 22 materials in early 2020 with the publication of Craig Bellamy’s doctoral thesis.
Since early 2020 my goal for the list has been to get this material wider visibility in the WW2 history community. By posting Section 22 materials from that thesis, and other list research, consistently on Twitter, I earned the list an invitation to the Bilge Pumps naval affairs podcast on the CIMSEC web site. That podcast is due to go up on their site 24 Feb 2021.
Today’s post will include slides 30 through 48 of 82 of the Section 22 information packet. This will include a spotlight on Section 22’s third Assistant Director, Cmdr. J.B. Jolley, USN reserve.

Commander J.B. Jolley USNR was with Section 22 early – at least from Oct 1943 from documents Craig Bellamy found in the Australian national archives. Current Statement #48 dated 24 October 1943 states that USN submarines (unnamed, darn it!) were being fitted with radar intercept receivers at that time. Cmdr. Jolley then ran Section 22 for a short time before and during the Leyte campaign (from about 4 September 1944 until at least the 10 Nov 1944) until his health failed. Yet that time, Section 22’s efforts under his leadership made its biggest contributions of WW2 and Jolley demonstrated a level of moral courage in his leadership that was unmatched in the Pacific War.
Yet, despite much research, our list has never found Cmdr Jolley’s first and middle names to go with his initials. This anonymity was part of the price Jolley paid for his moral courage as a leader, for he crossed Admiral Ernest King on the issue of Japanese radar tracking US ships and planes through their Mark III identification friend or foe (IFF) systems.
See Jolley’s IFF procedure at this link — ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USN/r at paragraph 11. IFF PROCEDURE sub-paragraph f. which is named in slide 30 below.
Adm. Turner, CENPAC’s amphibious forces commander, did not include anything like it in his Iwo Jima or Okinawa attack plans. And he knew far better…but did not want to draw Adm. King’s attentions.
To understand the context here, you have to know that electronic IFF was the US Navy’s technological turf in WW2. The U.S. Navy had created an IFF system before WW2, but the UK’s Mark III IFF was chosen for the sake of Allied commonality. And with radar centralized under Adm. King, IFF was part of his personal fief. King’s actions in the “Great South Pacific IFF Visitation” in Jan – Mar 1944 versus Section 22 made the combat failure of the Mark III IFF a failure in the same class as the Mark 14 torpedo and his own very personal tar baby.
Adm. King’s CIC magazine did not admit to what Jolley wrote into the Sept 1944 7th Fleet Leyte invasions until the March 1945 issue. Far too late for the intimidated Adm. Turner to add Cmdr. Jolley’s technique into the Okinawa invasion plans.
The combat failure of the Mark III IFF had to be made to go away…and it did…but that story is for coming “Section 22 Week” posts and slides.
The Computer Age Turns 75
In February 1946, the first general purpose electronic computer…the ENIAC…was introduced to the public. Nothing like ENIAC had been seen before, and the unveiling of the computer, a room-filling machine with lots of flashing lights and switches–made quite an impact.
ENIAC (the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was created primarily to help with the trajectory-calculation problems for artillery shells and bombs, a problem that was requiring increasing numbers of people for manual computations. John Mauchly, a physics professor attending a summer session at the University of Pennsylvania, and J Presper Eckert, a 24-year-old grad student, proposed the machine after observing the work of the women (including Mauchly’s wife Mary) who had been hired to assist the Army with these calculations. The proposal made its way to the Army’s liason with Penn, and that officer, Lieutenant Herman Goldstine, took up the project’s cause. (Goldstine apparently heard about the proposal not via formal university channels but via a mutual friend, which is an interesting point in our present era of remote work.) Electronics had not previously been used for digital computing, and a lot of authorities thought an electromechanical machine would be a better and safer bet.
Despite the naysayers (including RCA, actually which refused to bid on the machine), ENIAC did work, and the payoff was in speed. This was on display in the introductory demonstration, which was well-orchestrated from a PR standpoint. Attendees could watch the numbers changing as the flight of a simulated shell proceeded from firing to impact, which took about 20 seconds…a little faster than the actual flight of the real, physical shell itself. Inevitably, the ENIAC was dubbed a ‘giant brain’ in some of the media coverage…well, the “giant” part was certainly true, given the machine’s size and its 30-ton weight.
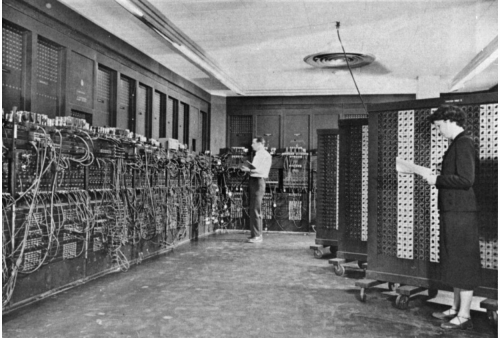
In the photo below, Goldstine and Eckert are holding the hardware module required for one single digit of one number.

The machine’s flexibility allowed it to be used for many applications beyond the trajectory work, beginning with modeling the proposed design of the detonator for the hydrogen bomb. Considerable simplification of the equations had to be done to fit within ENIAC’s capacity; nevertheless, Edward Teller believed the results showed that his proposed design would work. In an early example of a disagreement about the validity of model results, the Los Alamos mathematician Stan Ulam thought otherwise. (It turned out that Ulam was right…a modified triggering approach had to be developed before working hydrogen bombs could be built.) There were many other ENIAC applications, including the first experiments in computerized weather forecasting, which I’ll touch on later in this post.
Programming ENIAC was quite different from modern programming. There was no such thing as a programming language or instruction set. Instead, pluggable cable connections, combined with switch settings, controlled the interaction among ENIAC’s 20 ‘accumulators’ (each of which could store a 10-digit number and perform addition & subtraction on that number) and its multiply and divide/square-root units. With clever programming it was possible to make several of the units operate in parallel. The machine could perform conditional branching and looping…all-electronic, as opposed to earlier electromechanical machines in which a literal “loop” was established by glueing together the ends of a punched paper tape. ENIAC also had several ‘function tables’, in which arrays of rotary switches were set to transform one quantity into another quantity in a specified way…in the trajectory application, the relationship between a shell’s velocity and its air drag.
The original ‘programmers’…although the word was not then in use…were 6 women selected from among the group of human trajectory calculators. Jean Jennings Bartik mentioned in her autobiography that when she was interviewed for the job, the interviewer (Goldstine) asked her what she thought of electricity. She said she’d taken physics and knew Ohm’s Law; Goldstine said he didn’t care about that; what he wanted to know was whether she was scared of it! There were serious voltages behind the panels and running through the pluggable cables.
“The ENIAC was a son of a bitch to program,” Jean Bartik later remarked. Although the equations that needed to be solved were defined by physicists and mathematicians, the programmers had to figure out how to transform those equations into machine sequences of operations, switch settings, and cable connections. In addition to the logical work, the programmers had also to physically do the cabling and switch-setting and to debug the inevitable problems…for the latter task, ENIAC conveniently had a hand-held remote control, which the programmer could use to operate the machine as she walked among its units.
Notoriously, none of the programmers were introduced at the dinner event or were invited to the celebration dinner afterwards. This was certainly due in large part to their being female, but part of it was probably also that programming was not then recognized as an actual professional field on a level with mathematics or electrical engineering; indeed, the activity didn’t even yet have a name. (It is rather remarkable, though, that in an ENIAC retrospective in 1986…by which time the complexity and importance of programming were well understood…The New York Times referred only to “a crew of workers” setting dials and switches.)
The original programming method for ENIAC put some constraints on the complexity of problems that it could be handled and also tied up the machine for hours or days while the cable-plugging and switch-setting for a new problem was done. The idea of stored programming had emerged (I’ll discuss later the question of who the originator was)…the idea was that a machine could be commanded by instructions stored in a memory just like data; no cable-swapping necessary. It was realized that ENIAC could be transformed into a stored-program machine with the function tables…those arrays of rotary switches…used to store the instructions for a specific problem. The cabling had to be done only once, to set the machine up for interpreting a particular vocabulary of instructions. This change gave ENIAC a lot more program capacity and made it far easier to program; it did sacrifice some of the speed.
Welcome to “Section 22 Week” on Chicagoboyz, Day One of Six
General Headquarters, South West Pacific Area, Section 22 was a secret radar intelligence organization established under General Douglas MacArthur in World War II. This posts is the first in a series of six that will include the entire 82 slide information packet that I sent to the CIMSEC Bilge Pumps pod cast which was recorded this morning (Feb 19, 20201) and will “air” Feb 24, 2021
The beginnings of the secret Australian radar countermeasures unit during the Pacific War Feb 2020
Student thesis: Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) – CDU
This is my “2-minute elevator speech” thumb nail of Section 22’s historical role in WW2 in the Pacific theater versus Japan that I sent to the Bilge Pumps pod cast crew.
THE BIRTH, LIFE & DEATH OF MACARTHUR’S SECTION 22 RADAR HUNTERS
In the aftermath of the “Channel Dash” or Unternehmen Zerberus (Operation Cerberus) in February 1942, the Royal Australian Navy decided after a series of meetings that it needed a radio/radar countermeasures (the modern term of art is “electronic warfare”) section to prevent the Japanese from doing to them what the Germans did to the UK Royal Navy when it snuck the fast battleships Scharnhorst and Gneisenau and the heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen through the English Channel with the assistance of radio and radar jamming.
(See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Channel_Dash)
This RCM section was based in Sydney and administered from the RAN Office in Melbourne. It’s commander was Lt. Cdr. Joel Mace, RANVR(sp) (RANVR decodes as – “Royal Australian Navy Voluntary Reserve” special)
There was then a decision made — either supported or stage managed by Mace, according to one of the scholars on the E-mail list I administer — to move the organization to Brisbane under the control of the USN’s 7th Fleet in or before May 1943.
Then in June 1943 this “Radio and Radar Countermeasures Division” was taken over by MacArthur’s South West Pacific Area General Headquarters (SWPA GHQ) under the direct command of General Spencer Akins, MacArthur’s Chief Signals officer and one of the “Bataan Gang.” A group of trusted American officers who were at Bataan with MacArthur.
This informal decision was ratified in GHQ Operations Instructions No. 36 issued by MacArthur on 5 July 1943 and in November the group was christened “Section 22” based on it’s officer number in a Brisbane office building.
Section 22 encompassed and organized disparate RCM elements in the US Army, US Fifth Air Force, US 7th Fleet, Royal Australian Air Force, Royal Australian Navy, Australian Army into a coherent whole to deal with the Japanese deployment of radar in the Rabaul and South Pacific areas in 1942-1943.
The organization reached its full maturity in the Summer of 1944 (see photo above) after it absorbed the South Pacific theater’s RCM organizations, primarily in the 13th Air Force, Royal New Zealand Air Force and Royal New Zealand Navy. South Pacific Theater having become a rear area by that time.
Section 22 supported General MacArthur’s drive to the Philippines and had a role in mapping Japanese radar networks throughout New Guinea, the Dutch East Indies, the Philippines, South China, Formosa and the Ryukyus (including Okinawa) and the Japanese home islands (See May 1943 Rabaul map below).
Degrees of Toxicity
The Daughter Unit clued me in this week to a humongous ruckus which brewed among Air Force contributors to military-oriented discussion boards on Reddit a ruckus which involves the current Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force which for the laymen audience, means the very tippy-top enlisted, that singular and exemplary senior NCO who supposedly sits at the right hand of the highest military commanders in the land, to keep them appraised of the interests of the enlisted men and women. The Daughter Unit keeps track of this military ‘gen on a more regular basis than I do, as my two-decades long service was a good while ago, and I walked away from it all and constructed another life and long-term interests in writing, book-blogging and publishing. I will confess to some sentimental feelings for my service, as it provided me with a lot of fun, foreign travel, a decent paycheck and benefits (to include the pension and retirement benefits), a chance to hang out with some amazing people (as well as a soupcon of psychos, amiable freaks and the severely mal-adjusted), and a kind of mental grounding, even a rough sympathy when it comes to people who work for a living and get their hands dirty and their fingernails broken. But enough about me, and my not-particularly-rewarding career as an enlisted minion, toiling away in the bowels of the mighty military public affairs machine some two- or three-decades past.
The office of the Chief Master Sergeant of any service is a huge thing, in all the military forces: the name of the current Chief-Master-Whatever is one of the things military recruits to whatever branch are expected to know and recite on demand when in Basic Training. General officers there are, in legions, and the multi-stars roost en masse like grackles in the highest levels of command but there is only one Chief Enlisted, for all four (five counting the Coast Guard) military services. This one CMSAF JoAnne Bass is the first female to take up that exalted office for any of the services. I wish her the best luck in the world. When I began serving, there weren’t but a bare half-dozen of female senior enlisteds in the Air Force, and a fair number of the junior enlisted that I served with were the first or second females in certain traditionally male specialties which had just been opened to females. Unfortunately, as things are shaping up in the first months of her tour of duty, Chief Bass had better buckle in, as it looks like it’s going to be a bumpy flight. She put her foot wrong, straight off the bat, when a young NCO (innocently, or perhaps not so innocently) inquired on the CMSAF’s FB page as to how her last name was pronounced like the fish or the musical instrument?