|
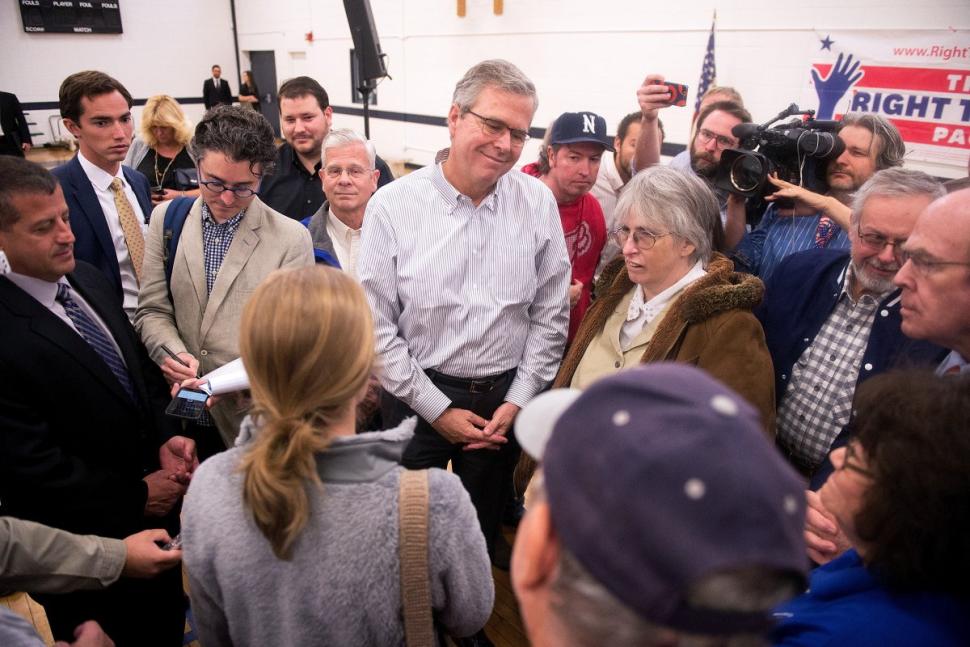
| Mao Zedong writing On Protracted Warfare (Yan’an, 1938) Source: Wikimedia. |
This essay was originally published at The Scholar’s Stage on 26 May, 2015. Because of its length it has been divided into two posts, both lengthy in their own right. This–the first of these two posts–is republished here at Chicago Boyz with little alteration. The second half of the essay shall be posted here later this week.
Last fall I wrote a popular series of posts outlining the history of the eight decade war waged between the Chinese Han Dynasty and the Xiongnu (old style: Hsiung-nu) nomadic empire. My posts were a response to a prominent American strategic theorist who misunderstood the history of the Han-Xiongnu relations in his search for enduring patterns in China’s military and diplomatic history relevant to China’s foreign relations today. Unfortunately, this experience was not a singular event. It seems that every month some new book or article is published pushing a misleading version of Chinese history or a strained interpretation of classical Chinese political thought to shore up a new theory of what makes China tick. I could devote this blog solely to refuting these poorly sourced theories and never run out of things to write about.
Despite these errors, I have a great deal of sympathy for those who pen them. They face a nearly insurmountable problem: many of the thinkers, strategists, and conflicts most important to the Chinese strategic tradition have next to nothing in English written about them. Critical works have yet to be translated, translated works have yet to be analyzed, histories of important wars and figures have yet to be written, and what has been written is often scattered in obscure books and journals accessible only to experienced Sinologists. English speakers simply do not have access to the information they need to study the Chinese strategic tradition.
This needs to change. It needs to change both for the sake of strategic theory as a discipline, which has essentially ignored the insights and observations gleaned from 3,000 years of study and experience, and for understanding the intentions of our rivals and allies in East Asia, who draw upon this tradition to decide their own political and strategic priorities. But in order to make these necessary changes we need a clear picture of where we are now. This essay attempts to provide this picture. It is not a bibliographic essay per say, for I will freely admit that I have not read all of the books and research articles I will mention below. Some titles I have only read in part; others I have not read at all. However, the goal of this post is not to review the results and conclusions of all these works, but to outline where research has been done and where more research is needed. For this purpose awareness suffices when more intimate knowledge is lacking.
Mastering 3,000 years of intellectual and military history is a gargantuan task. But in order to find the answers to some of the questions inherent in the study the Chinese strategic tradition, it must be done. I make no such claim of mastery. My expertise is uneven; I am most familiar with both the strategic thought and the actual events of the China’s classical period (Warring States through the Three Kingdoms era, c. 475 BC-280 AD), and am probably weakest when discussing the first two decades of the 20th century, a time critical to the development of the tradition but difficult to master because of the number of political actors involved, the complexity of their relations, and the great intellectual variety of the era. Despite these weaknesses I know enough to chart out the broad outlines of current scholarship, a charge most specialists in strategic theory cannot attempt and most Sinologists would not desire. These biases and proclivities have kept the two disciplines far apart; there is an urgent need for these two scholarly bodies to draw together. If this essay–which is addressed primarily to the first group but should be accessible to second–helps in some small way to bring this to pass I shall consider it a grand success.
This essay shall have three parts divided over two posts. The final section is a list of recommendations on how to establish and develop the study of the Chinese strategic tradition as an academic sub-field, as well as some thoughts on where individual Anglophone scholars might focus their research. The two earlier sections will review what has been published in English about the Chinese strategic tradition already. The term “the Chinese strategic tradition” is usually used in reference to the thinkers and the theorists of Chinese history, not the commanders and ministers who actually implemented policy. In the West this is almost always how the topic is discussed. Texts like Sun-tzu’s Art of War (hereafter, the Sunzi) are dissected with little reference to the way its thought was consciously implemented by those who studied it most carefully. This is a mistake. Most of the pressing questions in this field can only be answered by looking at how Chinese soldiers and statesmen actually behaved, and most of the errors common to Western punditry can be sourced to this tendency to ignore actual events in favor of theory. [1] In the case of ancient histories–whose account of events were highly stylized and moralizing–this distinction blurs. However, for the sake of organization I shall maintain the distinction between strategic thought (a subset of intellectual history) and strategic practice (a subset of diplomatic, political, and military history), covering each in turn.