Way back in the 50s and as Lex would say, “when I was a wee nubbit”, we had a Beagle named Sam. And like most Beagles, he loved to roam whenever the chance presented itself, such as a front door not closed fast enough. When that happened, the task to retrieve him fell upon me. I would chase him down the street of our Studio City neighborhood and at that young age learned there was only one thing that he liked even more than roaming – food.
The Smearing of Tulsi Gabbard
So the other night as I was watching CNN I had a revelation. CNN? My excuse was that I was at the gym, working off a cross-country plane flight, and CNN is right next to the NFL Network on the row of TVs.
Not many people watch CNN anymore. However, for those who are the “right” (or I should say “Left”) people, CNN and other media outlets serve as the rear guard protecting the retreating rout of the broken post-election leftist army. As such they are worth watching, though perhaps not as much as the replay of last year’s 49ers-Packers game on the TV next to it.
I have to admit I stopped watching the game, started focusing on CNN, and then ended up applauding a master stroke of intrigue that would have rivaled that of the royal courts of old.
Making Their Mark on the World
I’ve been mulling over the following question: how did each of the modern presidents from Nixon to present impact the world the most?
Richard Nixon: Opening relations with the People’s Republic of China.
Gerald Ford: The Helsinki Accords. The human rights plank encouraged the growing dissident movements in the Eastern Bloc. They took seriously what the Soviets were willing to put on paper in the albeit non-binding resolution.
Jimmy Carter: Enabling the Islamic totalitarian revolution in Iran.
Ronald Reagan: Fomenting the end of the Cold War. “Reagan bolstered the U.S. military might to ruin the Soviet economy, and he achieved his goal” – Gennady Gerasimov
George H. W. Bush: This may be a controversial choice, but I’m going with the “New World Order” speech, or rather what it represents – encouraging the United Nations to take a more active role in foreign relations. One of the legacies of the UN is the enshrinement of the ethic that wars must never be won, only fought to the point of ceasefire.
Bill Clinton: Granting the People’s Republic of China access to supercomputer technology vital to targeting manned, unmanned, and munitions-bearing rocketry. It’s the one great leap forward in China that actually worked.
George W. Bush: The Iraq War. Aside from altering the geopolitical landscape in the region, it convinced Muhammar Qaddafi to cooperate with the US to end Libya’s WMD program.
Barack Obama: Opening Iran to financial markets, thus magnifying its ability to conduct proxy wars.
Donald Trump (first term): It may be a bit early to gauge the legacy of the Abraham Accords, but opening the door to Israeli cooperation with some of its Arab neighbors is bound to have significant impact on Iran’s regional ascendency. It also breaks from the stupid tradition that any negotiations between Israel and any of its neighbors must include the Palestinians, as if Palestinian and non-Palestinian relations can’t be delt with separately.
Joe Biden: Opening Iran to financial markets, thus magnifying its ability to conduct proxy wars – assuming the Ukraine Missile Crisis does not top this. (Our own Trent Telenko is cited in the linked article.)
Lighted Airways and the Radio Range (updated)
When airplanes first started to be used for serious transportation purposes, sometime after World War I, the problems involved with flight at night and in periods of low visibility became critical. Transcontinental airmail, for example, lost much of its theoretical speed advantage if the plane carrying the mail had to stop for the night. Gyroscopic flight instruments addressed the problem of controlling the airplane without outside visual references, but there remained the problem of navigation.
An experiment in 1921 demonstrated that airmail could be successfully flown coast-to-coast, including the overnight interval, with the aid of bonfires located along the route. The bonfires were soon displaced by a more permanent installation based on rotating beacons. The first lighted airway extended from Chicago to Cheyenne…the idea was that pilots of coast-to-coast flights could depart from either coast in early morning and reach the lighted segment before dusk. The airway system rapidly expanded to cover much of the country–by 1933, the Federal Airway System extended to 18,000 miles of lighted airways, encompassing 1,550 rotating beacons. The million-candlepower beacons were positioned every ten miles along the airway, and in clear weather were visible for 40 miles. Red or green course lights at each beacon flashed a Morse identifier so that the pilot could definitely identify his linear position on the airway.
Lighted airways solved the navigation problem very well on a clear night, but were of limited value in overcast weather or heavy participation. You might be able to see the beacons through thin cloud or light rain, but a thicker cloud layer, or heavy rain/snow, might leave you without navigational guidance.
The answer was found in radio technology. The four-course radio range transmitted signals at low frequency (below the AM broadcast band) in four quadrants. In two of the quadrants, the Morse letter N (dash dot) was transmitted continuously; in the other two quadrants, there was continuous transmission of the Morse A (dot dash.) The line where two quadrants met formed a course that a pilot could follow by listening to the signal in his headphones: if he was exactly “on the beam,” the A and the N would interlock to form a continuous tone; if he was to one side or the other, he would begin to hear the A or N code emerging.
The radio range stations were located every 200 miles, and were overlaid on the lighted airways, the visual beacons of which continued to be maintained. The eventual extent of the radio-range airway system is shown in the map below. All that was required in the airplane was a simple AM radio with the proper frequency coverage.
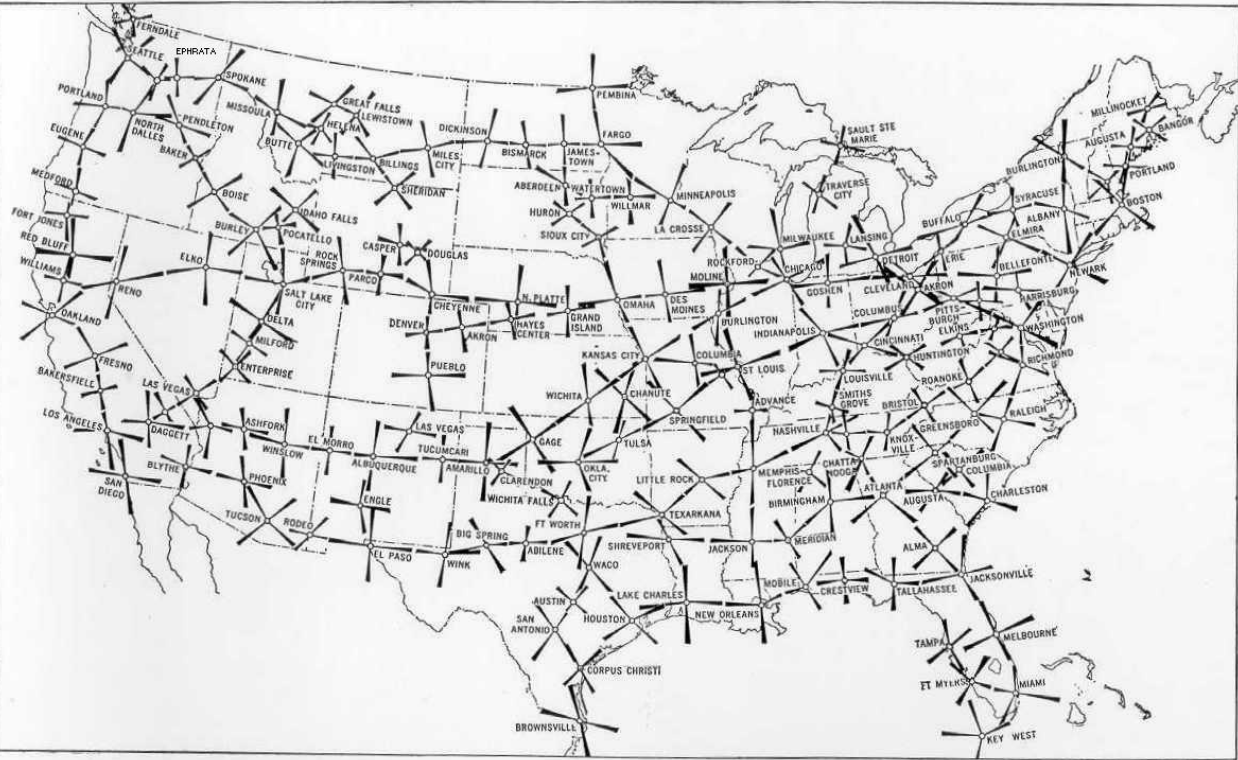
The system made reliable scheduled flying a reality, but it did have some limitations. Old-time pilot Ernest Gann described one flight:
Beyond the cockpit windows, a few inches beyond your own nose and that of your DC-2’s, lies the night. Range signals are crisp, the air smooth enough to drink the stewardess’s lukewarm coffee without fear of spilling it…Matters are so nicely in hand you might even flip through a magazine while the copilot improves his instrument proficiency…
Suddenly you are aware the copilot is shifting unhappily in his seat. “I’ve lost the range. Nothing.”
You deposit the Saturday Evening Post in the aluminum bin which already holds the metal logbook and skid your headphones back in place…There are no signals of any kind or the rap of distance voices from anywhere in the night below. There is only a gentle hissing in your headphones as if some wag were playing a recording of ocean waves singing on a beach.
You reach for a switch above your head and flip on the landing lights. Suspicion confirmed. Out of the night trillions of white lines are landing toward your eyes. Snow. Apparently the finer the flakes the more effective. It has isolated you and all aboard from the nether world. The total effect suggests you might have become a passenger in Captain Nemo’s fancy submarine.
My Name is Academe, and I’m a Failure.
I have been calling attention for years, and don’t mind at all when people with bigger platforms than mine recognize that the first step in correcting failure is to admit failure. The refreshingly solid Republican victories in national election might be the sort of evidence that would encourage academicians to revise their priors. Let’s start with Michael Clune, professor of English at Case Western, with “We Asked for It” in the house organ for business as usual.
Over the past 10 years, I have watched in horror as academe set itself up for the existential crisis that has now arrived. Starting around 2014, many disciplines — including my own, English — changed their mission. Professors began to see the traditional values and methods of their fields — such as the careful weighing of evidence and the commitment to shared standards of reasoned argument — as complicit in histories of oppression. As a result, many professors and fields began to reframe their work as a kind of political activism.
In reading articles and book manuscripts for peer review, or in reviewing files when conducting faculty job searches, I found that nearly every scholar now justifies their work in political terms. This interpretation of a novel or poem, that historical intervention, is valuable because it will contribute to the achievement of progressive political goals. Nor was this change limited to the humanities. Venerable scientific journals — such as Nature — now explicitly endorse political candidates; computer-science and math departments present their work as advancing social justice. Claims in academic arguments are routinely judged in terms of their likely political effects.
The costs of explicitly tying the academic enterprise to partisan politics in a democracy were eminently foreseeable and are now coming into sharp focus.
Democracy is about emergence in government. The academic enterprise is about emergence in understanding. It sounds like I got out just before the real nonsense took over. Or perhaps higher education reverted to its roots in the seminary. (Is it any accident, dear reader, that Joe Stalin was a seminarian at one time?)